### Summary: In a high-stakes military operation dubbed 'Operation Midnight Hammer,' the US targeted Iran’s nuclear facilities using advanced B-2 stealth bombers and various tactical decoys. The intricacies of this mission, conducted under the radar, reveal both successful strikes and ongoing uncertainties regarding the operation's effectiveness against Iran's nuclear capabilities.
### Title: US Executes Operation Midnight Hammer: A Strategic Strike on Iran’s Nuclear Facilities
### Title: US Executes Operation Midnight Hammer: A Strategic Strike on Iran’s Nuclear Facilities
### Description: The Pentagon details a complex aerial assault involving B-2 bombers and decoy aircraft aimed at critical nuclear sites in Iran.
---
An extensive military operation named 'Operation Midnight Hammer' has been executed by the United States, targeting Iran’s nuclear facilities. This methodically planned mission involved B-2 stealth bombers that departed from Whiteman Air Force Base on a complex journey to penetrate Iranian defenses, as described by General Dan Caine, Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, during a recent Pentagon briefing.
The operation commenced shortly after midnight, coinciding with a significant briefing led by Secretary of Defense Pete Hegseth, along with President Trump and other key officials. Concealed under the cover of night, seven B-2 bombers took flight towards Iran, armed with specialized bunker-buster bombs designed to penetrate deep underground facilities.
While the world’s attention initially focused on the Pacific as reports of military maneuvers in Guam surfaced, this was a strategic diversion. Pentagon sources claimed that this was a decoy operation, misleading observers about the actual target flights heading for Iran. As General Caine noted, the substantial nature of the bombing campaign relied on meticulous planning, aimed at avoiding detection and engaging minimal communication to reduce exposure.
After transiting across the Atlantic and reaching Iran's airspace with minimal resistance reported, the bombers executed tightly coordinated maneuvers. U.S. officials highlighted the lack of response from Iranian air defenses, with experts suggesting Israel's intelligence and air dominance played a pivotal role in ensuring the success of the aerial strike.
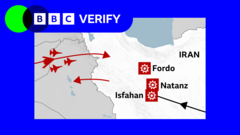
Commencing at approximately 18:40 EDT, the B-2s deployed their GBU-57 Massive Ordnance Penetrators (MOPs) at the Fordo facility and a second site at Natanz, marking the first use of these bombs in a combat scenario. Concurrently, Tomahawk missiles launched from U.S. submarines targeted the Isfahan nuclear site, creating a synchronized offensive aimed at multiple key locations.
The entire operation saw the utilization of around 75 precision-guided munitions and involved a total of 125 U.S. aircraft. While the Pentagon has hailed the mission as a decisive success, asserting it has severely impacted Iran's nuclear ambitions, the actual extent of damage and future implications remain uncertain. Insightful assessments of the strikes are ongoing, with experts emphasizing the operational complexities that characterized this unprecedented military engagement.
In conclusion, while Operation Midnight Hammer showcased a high level of tactical sophistication, its long-term influence on Iran's nuclear program continues to be a matter of debate among military analysts and international observers.
An extensive military operation named 'Operation Midnight Hammer' has been executed by the United States, targeting Iran’s nuclear facilities. This methodically planned mission involved B-2 stealth bombers that departed from Whiteman Air Force Base on a complex journey to penetrate Iranian defenses, as described by General Dan Caine, Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, during a recent Pentagon briefing.
The operation commenced shortly after midnight, coinciding with a significant briefing led by Secretary of Defense Pete Hegseth, along with President Trump and other key officials. Concealed under the cover of night, seven B-2 bombers took flight towards Iran, armed with specialized bunker-buster bombs designed to penetrate deep underground facilities.
While the world’s attention initially focused on the Pacific as reports of military maneuvers in Guam surfaced, this was a strategic diversion. Pentagon sources claimed that this was a decoy operation, misleading observers about the actual target flights heading for Iran. As General Caine noted, the substantial nature of the bombing campaign relied on meticulous planning, aimed at avoiding detection and engaging minimal communication to reduce exposure.
After transiting across the Atlantic and reaching Iran's airspace with minimal resistance reported, the bombers executed tightly coordinated maneuvers. U.S. officials highlighted the lack of response from Iranian air defenses, with experts suggesting Israel's intelligence and air dominance played a pivotal role in ensuring the success of the aerial strike.
Commencing at approximately 18:40 EDT, the B-2s deployed their GBU-57 Massive Ordnance Penetrators (MOPs) at the Fordo facility and a second site at Natanz, marking the first use of these bombs in a combat scenario. Concurrently, Tomahawk missiles launched from U.S. submarines targeted the Isfahan nuclear site, creating a synchronized offensive aimed at multiple key locations.
The entire operation saw the utilization of around 75 precision-guided munitions and involved a total of 125 U.S. aircraft. While the Pentagon has hailed the mission as a decisive success, asserting it has severely impacted Iran's nuclear ambitions, the actual extent of damage and future implications remain uncertain. Insightful assessments of the strikes are ongoing, with experts emphasizing the operational complexities that characterized this unprecedented military engagement.
In conclusion, while Operation Midnight Hammer showcased a high level of tactical sophistication, its long-term influence on Iran's nuclear program continues to be a matter of debate among military analysts and international observers.





















